We are living in a world of virtualization without actually knowing the driving force behind virtualization. In this article we will try to explain and explore Hypervisor based virtualization.
Understanding the need for Virtualization
Have you ever wondered what does it take to deploy an application? Yes, all it require is server with adequate Compute, Network and Storage. Having enough capacity in the pool to support the application is the key. However most of the techies get it wrong. Opting for physical server with static capacity is always tricky since the pattern of traffic is unknown during the initial stage of business.
Virtualization on the other hand helps you to dynamically allocate resources required for the application by having multiple server in the pool with diff/same configuration.
How do you virtualize the server?
Hypervisor, which is also called a virtual machine manager or VMM, is software that creates and runs virtual machines (VMS). The hypervisor is a hardware virtualization technique that allows multiple guest operating systems to run on a single host system at the same time.

Let’s assume that we have a server with 16 GB of RAM, 8 core processor and 5 TB of storage.
If you are running an application on standalone server there is a high chances of resources being underutilized or over utilized. How do we overcome such problem?
Of course the solution to this problem is provided by “Hypervisor”
Benefits of using Hypervisors
- Cloud computing wouldn’t be possible without virtualization. Virtualization wouldn’t be possible without the hypervisor. This layer of software supports the entire cloud ecosystem.
- It helps you to share the hardware resource with multiple server in the form of virtual machine.
- You would be able to dynamically allocate the underlying resources to the virtual machine based on the application requirement.
- It helps you to save the cost by encouraging optimal utilization of resource.
How Does Hypervisors Work?
Hypervisors support the creation and management of virtual machines (VMs) by abstracting a computer’s software from its hardware. Hypervisors make virtualization possible by translating requests between the physical and virtual resources.
Types of Hypervisors?
There are two types of Hypervisors. They are also referred to as native or bare Metal Hypervisors (Type 1) and Hosted Hypervisors (Type 2).
-
Type 1 Hypervisors (Bare metal or Native)
Type 1 hypervisors run directly on the host machine’s hardware, without the intervention of an underlying Operating System. It’s a virtualization layer lies between hardware and operating system. This means that the hypervisor has direct hardware access without contending with the Operating System and drivers. The virtualization will partition the physical resources into a multiple virtual machines.
Examples of Type 1 hypervisors include VMware ESXi, Citrix XenServer, and Microsoft Hyper-V hypervisor.
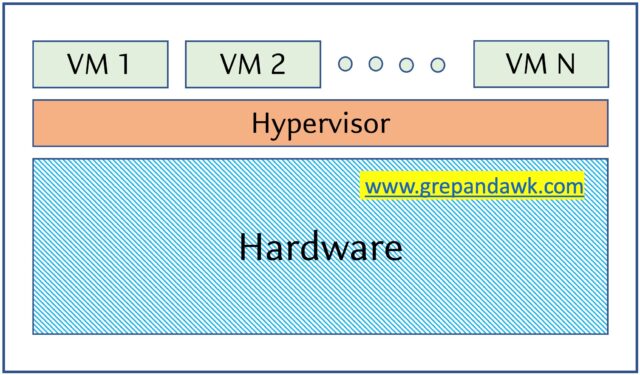
Pros & Cons of Type-1 Hypervisor:
Pros: Such kinds of hypervisors are very efficient because they have direct access to the physical hardware resources (like CPU, Memory, Network, Physical storage). This causes the empowerment of the security because there is nothing any kind of third-party resource so that attacker couldn’t compromise with anything.
Cons: One problem with Type-1 hypervisor is that they usually need a dedicated separate machine to perform its operation and to instruct different VMs and control the host hardware resources.
-
Type 2 Hypervisors (Hosted or Embedded)
A Host operating system runs on the underlying physical server. On top of the host operating system type 2 hypervisor would be installed to further create the virtual machine of different O.S operating system.
It is also known as ‘Hosted Hypervisor”. Such kind of hypervisors doesn’t run directly over the underlying hardware rather they run as an application on top of a Host operating system. Hypervisor asks the operating system to make hardware calls.
Example of Type 2 hypervisor includes Oracle Virtual box, VMware Fusion.
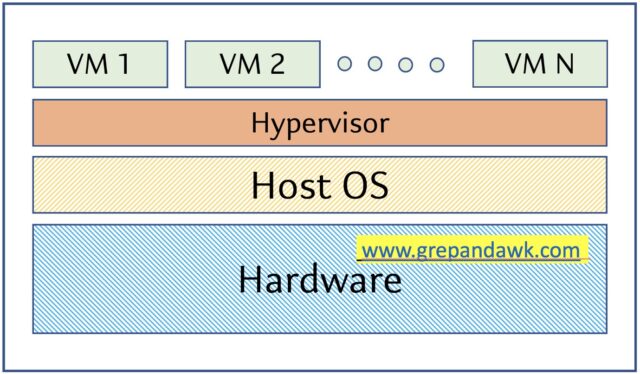
Pros & Cons of Type-2 Hypervisor:
Pros: Such kind of hypervisors allows quick and easy access to a guest Operating System alongside the host machine running. These hypervisors usually come with additional useful features for guest machines. Such tools enhance the coordination between the host machine and the guest machine.
Cons: Here there is no direct access to the physical hardware resources so the efficiency of these hypervisors lags in performance as compared to the type-1 hypervisors, and potential security risks are also there an attacker can compromise the security weakness if there is access to the host operating system so he can also access the guest operating system.
How does it help in Cloud Computing?
- Cloud is all about virtualization. Virtualization of server plays an important role.
- Cloud service providers uses hypervisor to create virtual machine to meet the client requirement.
- Hypervisors are a key element of the technology that makes cloud computing possible. Hypervisors make cloud-based applications available to users across a virtual environment while still enabling IT to maintain control over a cloud environment’s infrastructure, applications, and sensitive data.
- Since a hypervisor is a software layer that enables one host computer to simultaneously support multiple VMs.
- As an integral part of a virtualization platform, a hypervisor can help migrate applications to the cloud quickly. As a result, enterprises can reap many benefits, including reduced hardware expenditures, increased accessibility and greater scalability, for a faster return on investment.
Writes: Our proud Interns from EWIT, Bangalore and Mangalore Institute of technology- Ashwal Shetty, Aditya Bagalkot, Neha Vadagi, Namratha Chikkalkar,
Mentored by: Grep & Awk Technologies


